
Introduction
Process injection is widely used technique to alter the defense mechanisms of the victim system while malicious code is running and to hide our process as it belongs to any other legit process ran by user or system itself. Process injection provides stealth. Since every operating system is different, the process injection methods for each OS also differ and in this article we will investigate mostly used process execution/injection methods in android with comparing them the injection methods in Windows.
1 - Infecting Zygote
Zygote
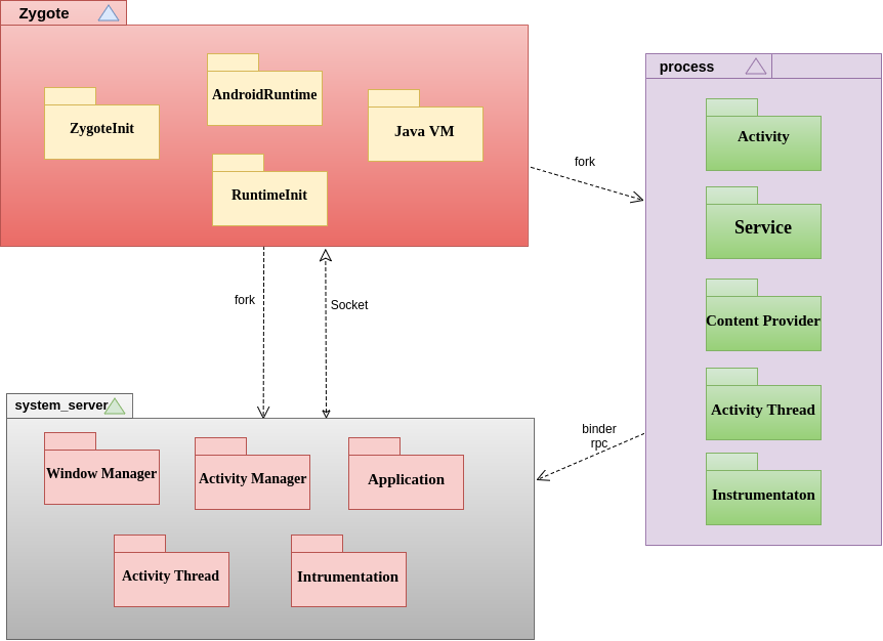
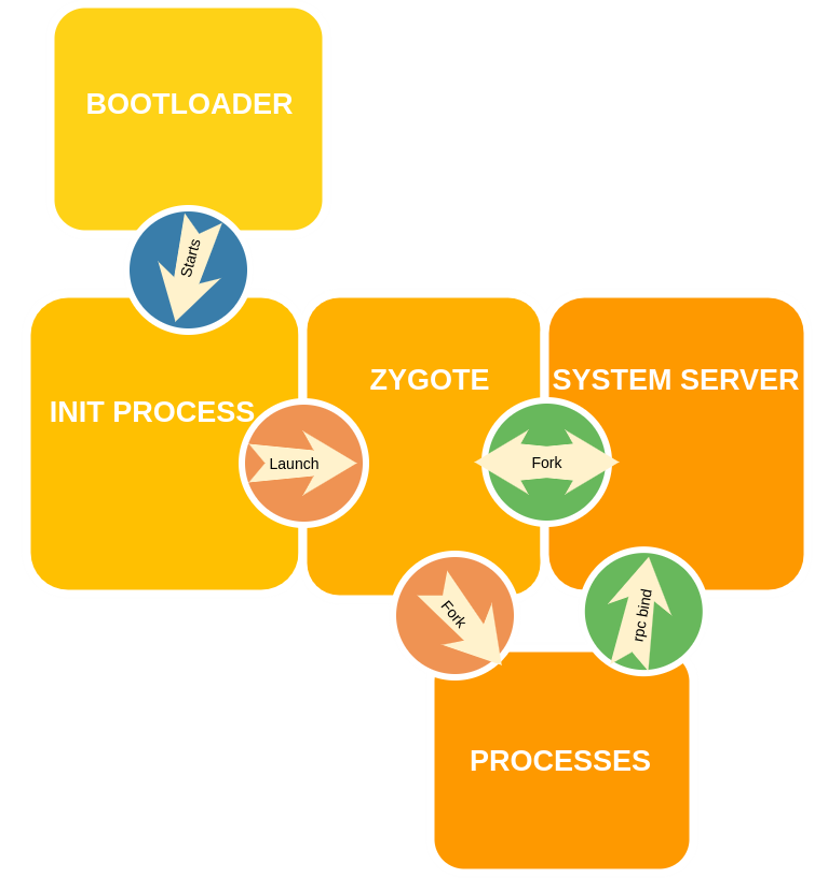
Zygote is a daemon responsible for launching apps. Once the system is booted Zygote is launched, the first Dalvik VM is created and once Zygote is launched, it preloads all needed resources and classes. Then Zygote starts System Server and opens a socket /dev/socket/zygote and listen for requests to start applications. When receives a request from this socket, it calls fork(). Once a process is forked, it clones itself but with the Linux kernel’s beautiful Copy On Write strategy, it doesn’t directly copy allocate another space in memory. When a process wants to edit the memory, the kernel will copy it and then let the process modify. So that, when other processes are forked from Zygote, the libraries without write permission are not copied and they all use the same ones. This means an injected library to Zygote will appear in all other applications launched after injection. But also malwares can inject the library to both Zygote and System Server and then restart the other processes to get them affected by the injection.
Since Zygote is the parent of all android applications and processes and considering the power of Zygote, the results of an attack directly to Zygote can be predicted.
In this technique, firstly after installation and launch of malware, it tries to root the device with using rooting exploits. Because also in this technique, malware still needs to use ptrace() to inject library and ptrace() function is restricted to root privileges.
Example malwares using this techniques are: CopyCat, Triada, Xiny.
Relation of Zygote - system_server and other processes is explained in the following visual to help understand the attack on Zygote.
2 - Code Injection with patching system libraries
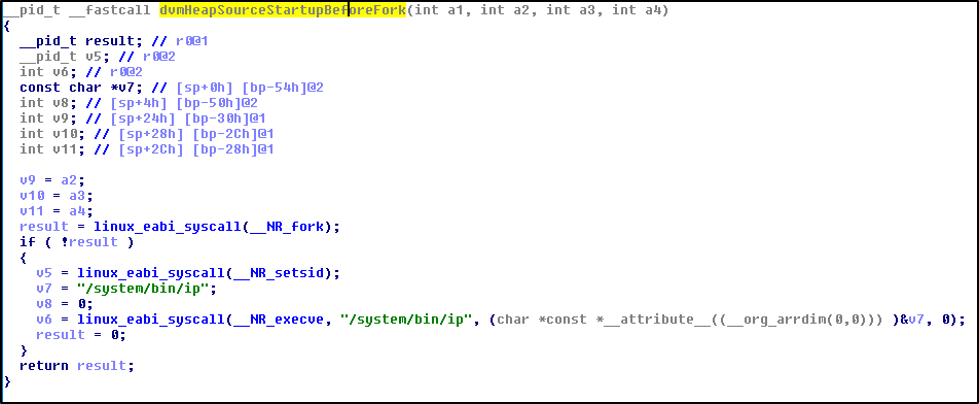
Once an app is launched, almost all classes are loaded thanks to Zygote. So that one can not override system class path, load custom classes with system class loader. But there is dvm library libdvm.so and ART library libandroid_runtime.so which can be infected. To be more specific In 2017 Android.Dvmap trojan used this method. Android.Dvmap searches for Android version and in Android 4.4.4 and/or older versions, it patches the libdvm.so library and specifically dvmHeapSourceStartupBeforeForkv method. In Android 5 and newer versions, patches libandroid_runtime.so, specifically nativeForkAndSpecialize method. It patches the method and after patch, method will only execute /system/bin/ip. Then malware also replaces original /system/bin/ip with previously crafted malicious one hidden in resources.
3 - Code Injection with injecting library to system libraries
In this injection type, malware tries to injects it malicious code with hiding it under a process of system process. In Linux systems one can easily inject any code or library with modifying LD_PRELOAD but in Android JVM is already forked from zygote once an app is running. So that it has to be done on runtime. It would be more clear and easy to understand with examining a sample trojan: Android.Loki.
The pioneer of this attack type was Android.Loki. Main target of Android.Loki is system_server process which is a special JAVA process with being the only process directly forked from Zygote as opposed to other processes created by ActivityManagerService ran in system_server. System_server is the first android process initiated by Zygote and it is the core process of Android responsible for starting core Android services such as ActivityManager, WindowManager etc. So that it is a powerful process capable of ptrace to processes and even killing zygote if necessary, you can find detailed information about system_server and given permissions to it here.
Initially Android.Loki reads file /proc/self/maps and searches for line that contains /system/lib/libc.so in this file. When it is found, trojan runs the following code:
inject(ss_pid, "/data/system/.loki/liblokih.so", "load_loki", "");
Ss_pid is the pid received from /proc/self/maps , which trojan will inject its code.
And injection is done with the help of ptrace() function which is a powerful function generally used by debuggers. It gives ability to kill a process, stop a process, manipulate memory and registers and may result in setting up breakpoints and patch the running code. Most injection techniques uses ptrace(), since in process injection, one needs to manipulate remote process and the most common way to do that is using ptrace() as almost all other Linux debuggers do.
In this example, trojan uses ptrace: PTRACE_ATTACH to attach to process, PTRACE_GETREGS and PTRACE_SETREGS to manipulate the process and inject liblokih.so library and lastly PTRACE_CONT to restart the process.
References
- https://securelist.com/attack-on-zygote-a-new-twist-in-the-evolution-of-mobile-threats/74032/
- https://anatomyofandroid.com/2013/10/15/zygote/
- http://www.androidauthority.com/first-android-malware-code-injection-778969/
- https://cphacker0901.wordpress.com/1900/11/21/talking-about-android-process/
- https://android.googlesource.com/platform/system/sepolicy/+/nougat-dr1-release/system_server.te
- https://vms.drweb.com/virus/?i=7954502&lng=en
- https://securelist.com/dvmap-the-first-android-malware-with-code-injection/78648/